參考價(jià)格
面議型號
100184品牌
先豐納米產(chǎn)地
江蘇樣本
暫無制作方法:
.質(zhì)量標(biāo)準(zhǔn):
.純度:
99.%目數(shù):
0.4-1微米品級:
一級看了Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的用戶又看了
 留言詢價(jià)
留言詢價(jià) 電話詢價(jià)
電話詢價(jià)

虛擬號將在 180 秒后失效
使用微信掃碼撥號
| 號 | CAS號 | 編號 | 包裝 | 參數(shù) |
| 100184 | 12138-09-9 | XF061 | 100g | 純度99% 粒徑范圍:0.4-1微米 |
平均粒徑范圍:0.4-1微米
純度> 99%
Average Particle Size: 0.4-1 microns
Purity: 99%
WS2 Micropowder is useful for creating WS2 solutions with applications ranging from electronics to energy storage. The powder may be sonicated in a range of liquid solvents, whereas the longer sonication takes place, the smaller the flake size in solution. Further, before sonication the solution will be silvery, and after it will turn a greenish-yellow. The solvents useful during sonication include benzyl benzoate, isopropanol, acetone, methanol, and many others.
The liquid dispersion may then be used to create a thin film on the substrate of your choosing. These thin-films have a range of applications, such as transistors, solar cells, and energy storage devices.
WS2 solution can also be used in composite materials.
The difference between our micropowders and ultrafine powders are their flake sizes. Ultrafine powders have smaller flakes, and create dispersions with smaller particle sizes after sonication than micropowder. Micropowders require more sonication and will result in flakes with larger lateral dimensions. Micropowder is a low-cost alternative to our ultrafine powder.
Transparent and Flexible Electronics
Transistors
Composite Materials
Chemical and bio-sensors
Semiconductor printable inks
Electrical Characteristics of Molybdenum Disulfide Flakes Produced by Liquid Exfoliation, Lee et al. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, pp. 4178-4182
Gelatin-assisted fabrication of water-dispersible graphene and its inorganic analogues, Ge et al. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, pp. 17619-17624
Preparation of High Concentration Dispersions of Exfoliated MoS2 with Increased Flake Size, O.Neill et al. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, pp. 2414-2421
Two-Dimensional Nanosheets Produced by Liquid Exfoliation of Layered Materials, Coleman et al. Science, 2011, 331, pp. 568-571
暫無數(shù)據(jù),!

利用負(fù)載型固體胺吸附劑從大型點(diǎn)源的實(shí)際煙道氣中捕獲CO2,因其高效,、便捷等特點(diǎn)被視為減少溫室氣體排放的重要技術(shù),。然而,在CO2吸附和脫附操作時(shí),,吸附劑需暴露在包含氧氣,、二氧化碳、水和氮?dú)獾葟?fù)雜成分的煙

Advanced Materials:通過調(diào)節(jié)水凝膠中的離子受限傳輸實(shí)現(xiàn)仿生視網(wǎng)膜2025年3月12日,,期刊Advanced Materials報(bào)道先豐客戶開發(fā)了一種基于雙層離子水凝膠的突觸器件,,用于
氧化石墨烯作為石墨烯材料的重要衍生物,,憑借其優(yōu)異的分散性和化學(xué)活性,在材料科學(xué),、能源,、生物醫(yī)學(xué)等領(lǐng)域展現(xiàn)出廣闊前景。作為先豐納米暢銷15年的經(jīng)典材料-氧化石墨烯,,從推出以來得到了眾多科研工作者的認(rèn)可,,
光熱治療(PTT)因其高選擇性,、最小副作用和精確的時(shí)空控制,,已成為應(yīng)對創(chuàng)傷感染的極具前景的方法,。近年來,各種光熱劑,,包括有機(jī)光熱劑,、金屬基納米材料、碳基納米材料和有機(jī)/無機(jī)納米復(fù)合材料,,已被探索用于破
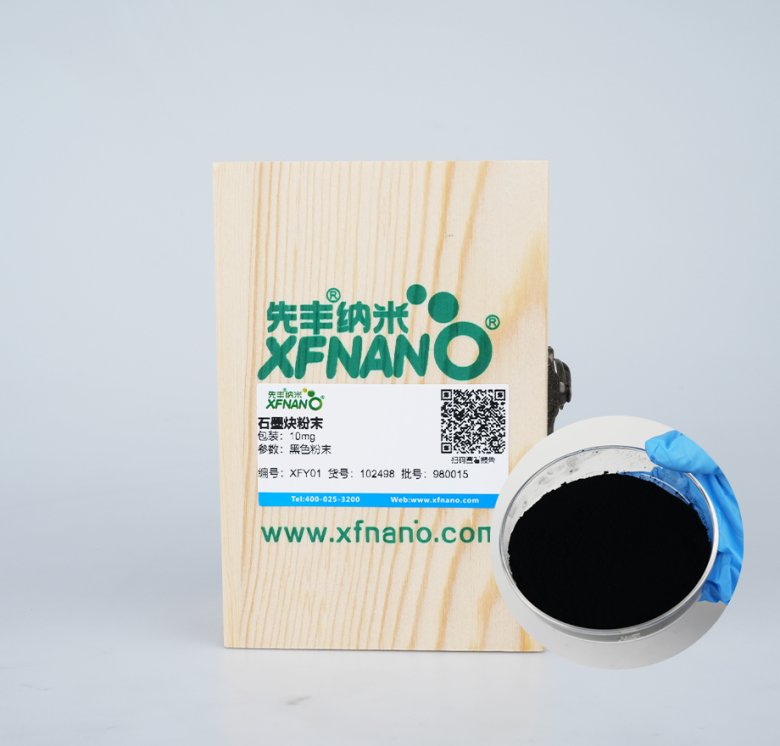

石墨炔(Graphdiyne ,,GDY) 是一種很有前途的碳同素異形體,,在各個(gè)學(xué)科中都引起了極大的興趣。作為一種新興的能量轉(zhuǎn)換材料,,GDY表現(xiàn)出區(qū)別于傳統(tǒng)碳材料的獨(dú)特結(jié)構(gòu)和性能,,在快充電池、氫能轉(zhuǎn)換等
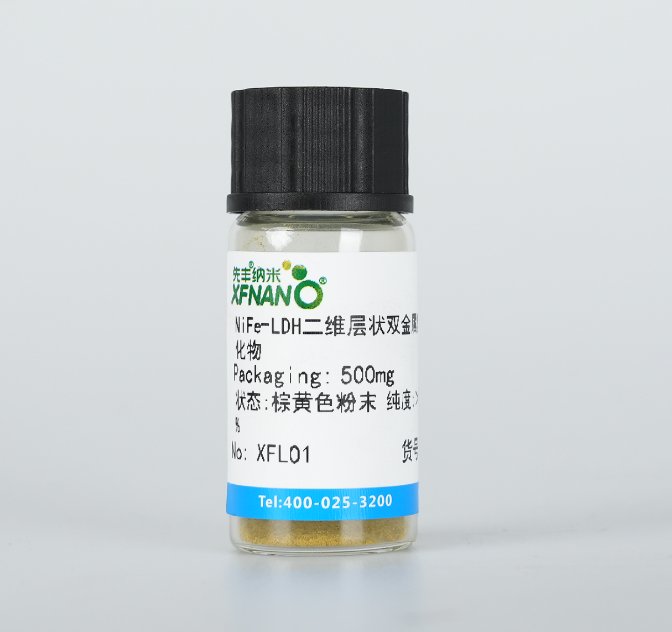

近年來,,層狀雙金屬氫氧化物(LDH)由于具有可調(diào)的化學(xué)組成、優(yōu)異的電子傳遞能力,、大的比表面積和孔隙率以及良好的穩(wěn)定性,,使得LDH在電催化領(lǐng)域展現(xiàn)出廣闊的應(yīng)用前景并多次登上各大頂刊,特別是在海水電解方面
 Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的工作原理介紹,?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的工作原理介紹,? Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的使用方法,?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的使用方法,? Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片多少錢一臺?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片多少錢一臺? Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片使用的注意事項(xiàng)
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片使用的注意事項(xiàng) Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的說明書有嗎,?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的說明書有嗎,? Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的操作規(guī)程有嗎,?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的操作規(guī)程有嗎,? Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的報(bào)價(jià)含票含運(yùn)費(fèi)嗎?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片的報(bào)價(jià)含票含運(yùn)費(fèi)嗎? Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片有現(xiàn)貨嗎,?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片有現(xiàn)貨嗎,? Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片包安裝嗎,?
Graphene Supermarket二硫化鎢微片包安裝嗎,? 手機(jī)版:
手機(jī)版: